>> Cell Theory Section << |
||
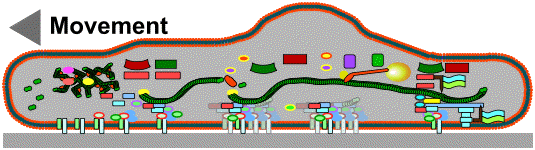
For the adressed purpose, the modification of the cell behavior by cell instruction via surfaces, a modular concept will be helpful. The modules cover the adhesion and the motility apparatus. It might appear somewhat selective but it is successful in the explanation of a member of different cell behaviors. Beneath the processes concerned there are migration, adhesion, phagocytosis and the cell communication by physical contact. The figure introduces into the basic functional and structural components of the model. A simpler draft is given as long as Your mouse is over the image. The single modules are explained in higher detail in the topics on the page. Click on the image for a higher resolution draft or click on the buttons to enter the topics. |
||
 |
||
 |
 |
|||